5 common health conditions that can lead to myalgia
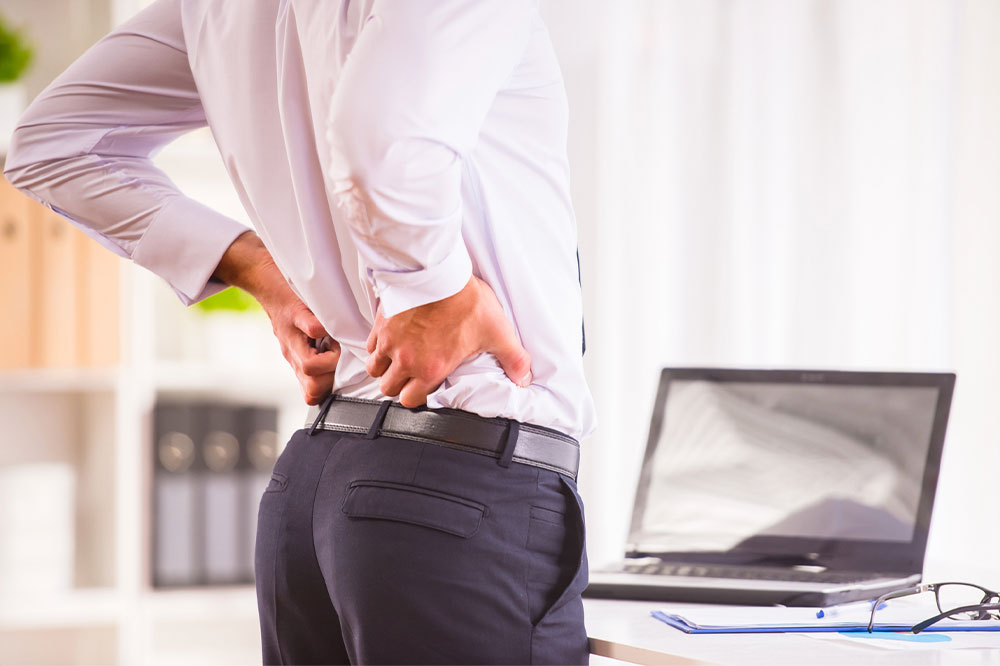

Most individuals are likely to experience myalgia (pain in the muscles) at some point during their lifetime. Studies show that 11% to 40% of adults in the country live with chronic pain. You might experience the sore, aching feeling in a small area or the whole body. The severity of the ache experienced may also vary. Several factors can lead to the development of this condition; here are five common causes.
5 health conditions that can trigger myalgia
Lupus
Lupus is a disease caused by the body’s immune system attacking its tissues and organs. The most noticeable symptom of the condition is a facial rash that looks like the wings of a butterfly opening across both cheeks. Lupus may lead to inflammation, which can affect various organ functions. However, each individual may experience different symptoms of the autoimmune disease. A common complication triggered by lupus is myalgia. The condition can also lead to inflammation in the muscles, most commonly in the thighs, upper arms, hips, and shoulders. Those with lupus may experience weakened muscles, making it difficult to raise their arms or stand up from a chair.
Strains
Several muscle pains are triggered by accidents that may bruise muscles in the body. However, an isolated muscle strain may also lead to excruciating pain. A muscle strain may occur when the muscle or tendon, which is the fibrous tissue that connects the muscle to bones, is injured. Strains are commonly experienced in the hamstrings (the muscles at the back of the thigh) and in the lower back. The pain might be mild if the muscle or tendon is overstretched. But a partial or complete tissue tear will lead to severe muscle pain.
Cold or flu
Cold and flu are viral infections that are known to cause myalgia. The immune system identifies harmful infections and releases white blood cells to fight off the bacteria. However, the overactive immune system can lead to uncontrollable muscle pains. The more the immune system works, the higher the intensity of muscle pains felt by the individual. This pain is usually seen in the chest, lungs, and throat. One may also develop body aches through other conditions, including fatigue, fever, polio, and general weakness.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that affects the joints in the body. Signs and symptoms of RA progress gradually and are easy to miss as they might appear to be symptoms of other health conditions. The condition may cause a 25% to 70% reduction in muscular strength. The muscles may become weak due to a deteriorating skeletal muscle mass, and individuals with RA have reported stiffness, tenderness, and pain in the respective muscles. The joints affected by the autoimmune disorder may also swell and feel warm to the touch.
Anemia
The red blood cells (RBCs) carry oxygen (hemoglobin) to the body’s tissues. However, an individual who suffers from anemia may lack such healthy RBCs. There are various types of anemia, including iron deficiency anemia. A low iron composition may result in the body not producing ample red blood cells. The resultant lack of oxygen may lead to tiredness and shortness of breath. People with an iron deficiency may also experience muscle pains due to insufficient oxygen in their muscles. Additionally, the low red blood cell count may cause toxins to accumulate in the muscle and lead to mild or severe myalgia.
Multiple treatments can help one manage and reduce myalgia and its symptoms. Oral prescriptions or injections are two common treatment methods recommended by healthcare experts. Another treatment option growing in popularity is prescription pain patches. These patches are available for back pains or cramps in regular or XL sizes. The pain relief prescriptions come with adhesive backs that can stick to the skin. Furthermore, these patches gradually release the treatment into the bloodstream, which curbs myalgia.