9 warning signs of sepsis

Sepsis is an inflammatory health condition caused by an adverse reaction to the chemicals released in the blood to fight an infection. Any wound that is left uncovered and untreated can become a breeding point for fungi and bacteria, increasing the risk of sepsis. It is estimated that about 1.7 million adults nationwide develop this condition, requiring immediate medical attention. So, here are some warning signs of sepsis one should not ignore:
Dizziness
A sepsis episode or septic shock involves a significant drop in blood pressure levels, which can cause extreme dizziness and disorientation.
Slurred speech and confusion
Reduced blood flow to the brain here can lead to slurred and incomprehensible speech. The effects of sepsis on the brain include intense chaos and confusion, which can worsen if the condition is left untreated.
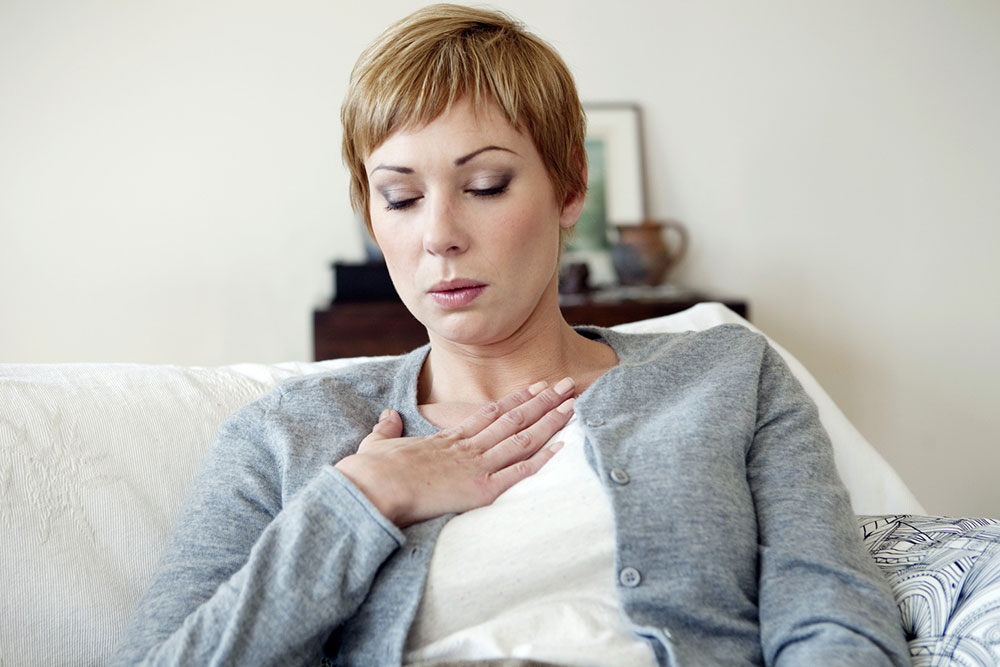
Shortness of breath
Sepsis may result in the inability to take in enough oxygen, causing shortness of breath. Some may also experience hyperventilation or rapid breathing.
Low urine output
Those with sepsis may experience multiple organ failure at advanced stages. Kidney failure may cause low urine output; in some cases, one may be unable to pass urine for a whole day.
Urinary tract infections
The infection associated with sepsis can start in the urinary tract. So, a UTI can be one of the warning signs of sepsis. The infection is characterized by painful urination and shivering.
High or low body temperature
Sepsis may trigger symptoms of pneumonia, including very high or low body temperatures, accompanied by chills and extreme fatigue.
Muscle pain and weakness
Sepsis is associated with muscle pain and weakness, which affects respiratory as well as limb muscles. This symptom is often attributed to muscle wasting brought on by the condition. This is why a meal plan rich in healthy fats and protein-rich foods is often recommended to enhance muscle strength when healing from this condition.
Increased heart rate
Blood flow to different parts of the body reduces with sepsis, making the heart exert more effort than usual and leading to an increased heart rate.
Seizures
Neurological complications resulting from sepsis may induce seizures or stroke. These seizures may be convulsive or non-convulsive and may worsen other symptoms.
While those with weakened immune systems are at a higher risk of developing sepsis, untreated minor cuts and infections can also increase the risk of the condition. So, it is important to have first-aid kits handy in homes and offices to treat wounds promptly and prevent infections.